简介
TextCNN 是利用卷积神经网络对文本进行分类的算法,由 Yoon Kim 于2014年在 “Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification” 一文中提出的算法。
原理图
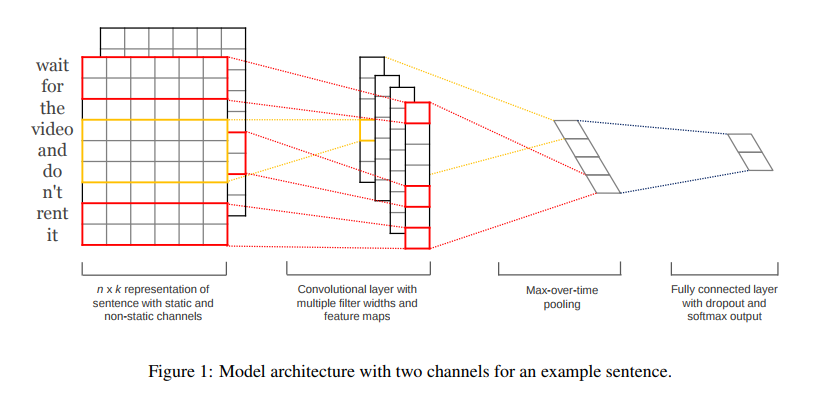
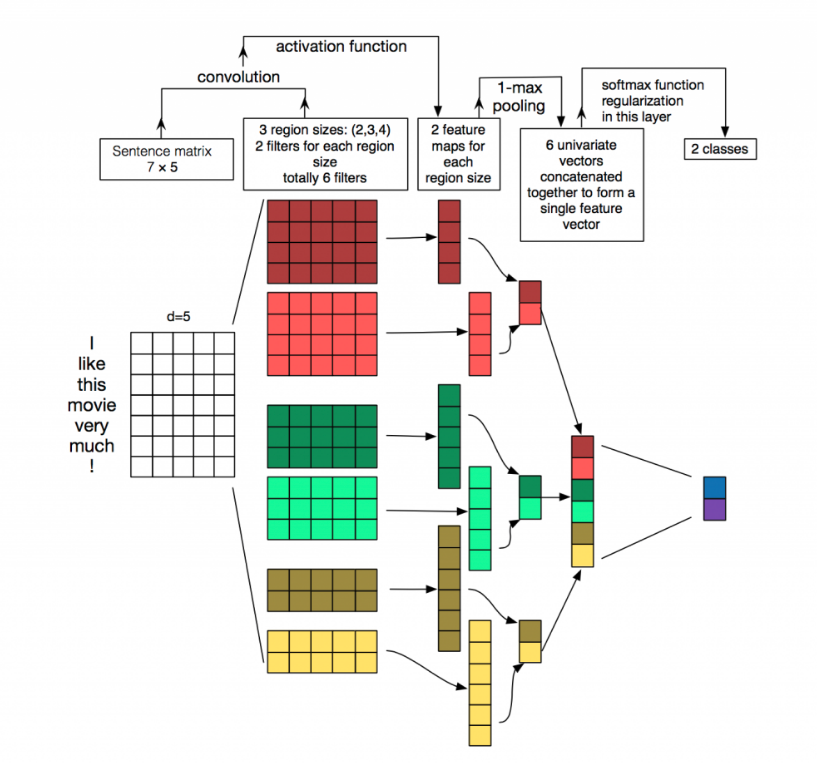
结构详解
第一层
第一层是输入的7*5的词向量矩阵,词向量的维度为5,共7个单词。
第二层
第二层是卷积层,共有6个卷积核,尺寸为2×5、3*5、4×5,每个尺寸各2个,输入层分别与6个卷积核进行卷积操作,再使用激活函数激活,每个卷积核都得到了对应的feature maps。
第三层
第三层是池化层,使用1-max pooling提取出每个feature map的最大值,然后进行级联,得到6维的特征表示。
第四层
第四层是输出层,输出层使用softmax激活函数进行分类,在这层可以进行正则化操作(l2-regulariation)。
细节介绍
feature
这里的特征就是词向量,词向量有静态和非静态的,静态的可以使用pre-train的,非静态的则可以在训练过程中进行更新,一般推荐非静态的fine-tunning方式,即以pre-train的词向量进行初始化,然后在训练过程中进行调整,它能加速收敛。
channel
图像中可以利用 (R, G, B) 作为不同channel,而文本的输入的channel通常是不同方式的embedding方式(比如 word2vec或Glove),实践中也有利用静态词向量和fine-tunning词向量作为不同channel的做法。
conv-1d
在TextCNN中用的是一维卷积(conv-1d),一维卷积带来的问题是需要设计通过不同size的filter获取不同宽度的视野。
1-max pooling
在TextCNN中用的是1-max pooling,当然也可以使用(dynamic) k-max pooling,在pooling阶段保留 k 个最大值,保留全局信息。
参数设置
- 序列长度:一般设置为最大句子的长度
- 类别数量:预测的类别的数量
- 字典大小:即词汇数量
- 嵌入长度:即每个词表示的词向量长度,训练词向量可以使用
- word2cec、fasttext、glove等工具
- 卷积核大小:对应n元语法的概念
- 卷积核个数:卷积核大小对应的卷积核个数
TextCNN实现
# coding: utf-8
import pickle
import logging
import tensorflow as tf
logging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s : %(levelname)s : %(message)s',level=logging.INFO)
class TextCNN(object):
"""
A CNN for text classification.
Uses an embedding layer, followed by a convolution, max-pooling and soft-max layer.
"""
def __init__(self, config):
self.lr = config['lr']
self.batch_size = config['batch_size']
# 词典的大小
self.vocab_size = config['vocab_size']
self.num_classes = config['num_classes']
self.keep_prob = config['keep_prob']
# length of word embedding
self.embedding_size = config['embedding_size']
# seting filter sizes, type of list
self.filter_sizes = config['filter_sizes']
# max length of sentence
self.sentence_length = config['sentence_length']
# number of filters
self.num_filters = config['num_filters']
def add_placeholders(self):
self.X = tf.placeholder('int32', [None, self.sentence_length])
self.y = tf.placeholder('int32', [None, ])
def inference(self):
with tf.variable_scope('embedding_layer'):
# loading embedding weights
with open('Text_cnn/embedding_matrix.pkl','rb') as f:
embedding_weights = pickle.load(f)
# non-static
self.W = tf.Variable(embedding_weights, trainable=True, name='embedding_weights',dtype='float32')
# shape of embedding chars is (None, sentence_length, embedding_size)
self.embedding_chars = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.W, self.X)
# shape of embedding char expanded is (None, sentence_length, embedding_size, 1)
self.embedding_chars_expanded = tf.expand_dims(self.embedding_chars, -1)
with tf.variable_scope('convolution_pooling_layer'):
pooled_outputs = []
for i, filter_size in enumerate(self.filter_sizes):
filter_shape = [filter_size, self.embedding_size, 1, self.num_filters]
W = tf.get_variable('W'+str(i), shape=filter_shape,
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1))
b = tf.get_variable('b'+str(i), shape=[self.num_filters],
initializer=tf.zeros_initializer())
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.embedding_chars_expanded, W, strides=[1,1,1,1],
padding='VALID', name='conv'+str(i))
# apply nonlinearity
h = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(conv, b))
# max pooling
pooled = tf.nn.max_pool(h, ksize=[1, self.sentence_length - filter_size + 1, 1, 1],
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='VALID', name="pool")
# shape of pooled is (?,1,1,300)
pooled_outputs.append(pooled)
# combine all the pooled features
self.feature_length = self.num_filters * len(self.filter_sizes)
self.h_pool = tf.concat(pooled_outputs,3)
# shape of (?, 900)
self.h_pool_flat = tf.reshape(self.h_pool, [-1, self.feature_length])
# add dropout before softmax layer
with tf.variable_scope('dropout_layer'):
# shape of [None, feature_length]
self.features = tf.nn.dropout(self.h_pool_flat, self.keep_prob)
# fully-connection layer
with tf.variable_scope('fully_connection_layer'):
W = tf.get_variable('W', shape=[self.feature_length, self.num_classes],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b = tf.get_variable('b', shape=[self.num_classes],
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
# shape of [None, 2]
self.y_out = tf.matmul(self.features, W) + b
self.y_prob = tf.nn.softmax(self.y_out)
def add_loss(self):
loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=self.y, logits=self.y_out)
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss)
tf.summary.scalar('loss',self.loss)
def add_metric(self):
self.y_pred = self.y_prob[:,1] > 0.5
self.precision, self.precision_op = tf.metrics.precision(self.y, self.y_pred)
self.recall, self.recall_op = tf.metrics.recall(self.y, self.y_pred)
# add precision and recall to summary
tf.summary.scalar('precision', self.precision)
tf.summary.scalar('recall', self.recall)
def train(self):
# Applies exponential decay to learning rate
self.global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
# define optimizer
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(self.lr)
extra_update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)
with tf.control_dependencies(extra_update_ops):
self.train_op = optimizer.minimize(self.loss, global_step=self.global_step)
def build_graph(self):
"""build graph for model"""
self.add_placeholders()
self.inference()
self.add_loss()
self.add_metric()
self.train()